Considering the current rate of population growth, it has been predicted that the global population will reach 9 billion by the year 2050; with the rise in population, one of the primary concerns is depleting resources. To overcome that search for sustainable production of food without depleting resources. The forerunner in that area is the industry where microbes are used more than normal, i.e. microbial technology. Microbes have been used in processes like fermentation from old age; nowadays, they are involved in waste reduction and alternative protein production, which allows them to play a vital role in the future of sustainable food production. By increasing the use and effectiveness of microbial powers, we can reduce waste production, create sustainable sources of protein, and improve agricultural efficacy without disturbing or depleting the current ecosystem. In this article, we will primarily focus on the role of microbes in sectors like fermentation, waste reduction, protein production, and improved agriculture sustainability, while also looking at the challenges and ethical considerations.
Microbes in Fermented Foods
Fermentation is the process through which microbes convert carbohydrates into simpler forms. The use of fermentation dates back to ancient Egypt, China and Israel, where it was primarily used as a method to store excess food or create beer. In the current age, its application is across numerous sectors. It has been proven that microbes in fermentation applications go beyond improving taste and preservation. Fermented foods have unique functional properties, imparting some health benefits to consumers due to the presence of functional microorganisms, which possess probiotic properties, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and peptide production, etc.

Microbes involved in fermentation can be bacteria, yeast or fungi.
While fermentation helps preserve food and enhance nutrition, microbes also play a crucial role in managing food waste on an even larger scale. In the next section, we’ll explore how microbes contribute to waste reduction and bioconversion.
Waste Reduction & Bioconversion
One-third of all food produced globally, close to 1.3 billion tons, is wasted every year. But what if it was possible that microbes could turn that waste into valuable resources? That is possible, as microbes are involved in the decomposition of organic matter, reducing pollutants and converting waste into valuable resources like compost or biogas. Common microbes involved in this are bacteria, fungi and certain algae. The table below gives a brief overview of their involvement and benefits.
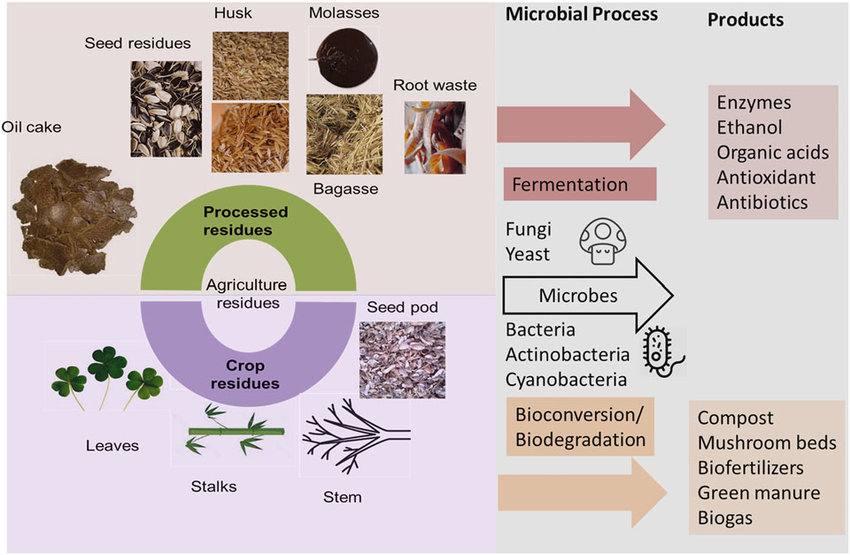
Beyond waste reduction, microbes are also reshaping how we produce protein. In the next section, we’ll explore how microbial proteins are emerging as a sustainable alternative to traditional protein sources.
Alternative Protein Sources
With the rise in general awareness among the public about how protein plays a huge role in our diet, the requirement for alternative sources of protein has increased among demographics like veganism and culturally restricted ones. To address that, certain companies have been involved in the race to develop a “vegan meat” that is eerily similar to real meat in taste, texture and sensory appeal. Among others, one of the ways was to use microbes to develop a better alternative.
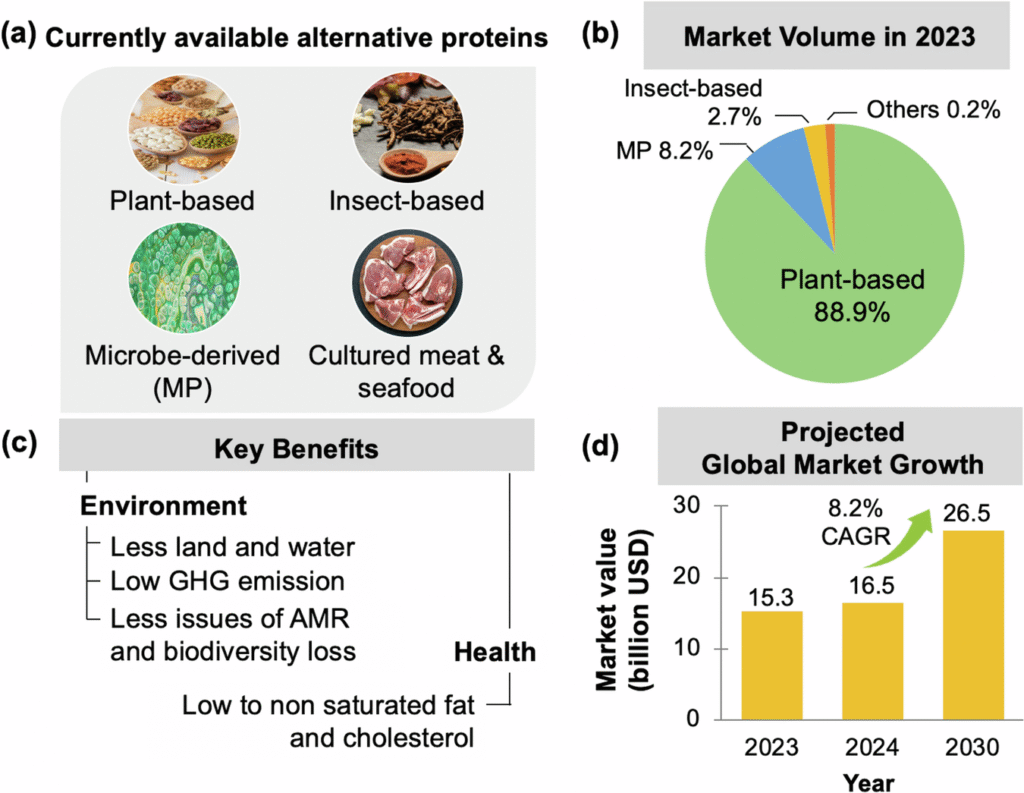
There are several advantages to this practice: It requires less land, water, and energy than livestock farming, High protein content & digestibility (compared to plant proteins), and reduces reliance on factory farming & deforestation.
Soil & Crop Sustainability
Microbes play a vital role in sustainable agriculture by enhancing soil fertility and crop resilience. Beneficial bacteria and fungi contribute to nitrogen fixation, phosphorus solubilization, and overall nutrient cycling, which reduces the dependence on synthetic fertilisers. Mycorrhizal fungi, for example, form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, improving water absorption and resistance to drought. Additionally, microbial biopesticides offer an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, reducing the environmental impact of conventional farming.
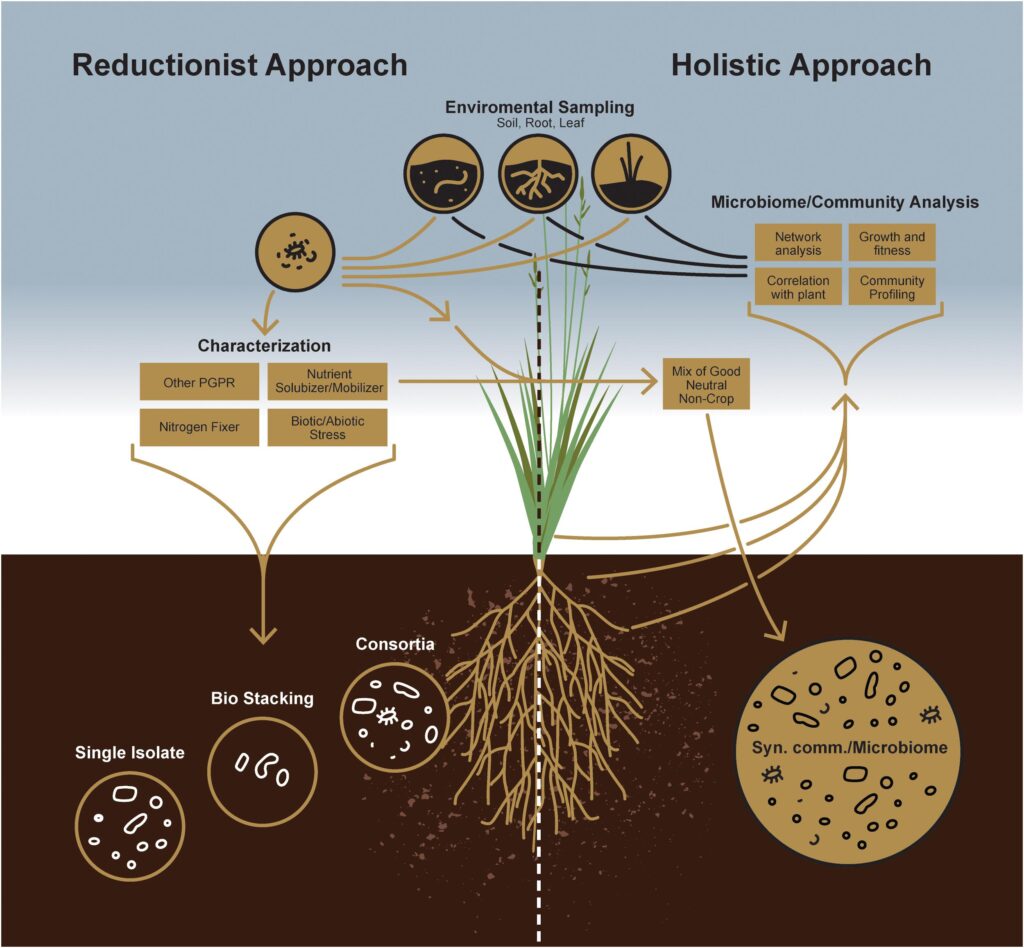
Bioremediation, another microbial application, helps cleanse soil contaminated by pollutants, ensuring safer and healthier agricultural land. As climate change continues to impact global food security, harnessing microbial potential in agriculture presents a sustainable path forward.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite their promising benefits, the use of microbes in food production and agriculture presents several challenges. Scaling up microbial protein production, ensuring consistent quality, and addressing regulatory concerns are key hurdles. Additionally, consumer acceptance remains a significant challenge, as some people are hesitant to embrace foods derived from microbes.
From an ethical standpoint, there is a need to balance innovation with safety and sustainability. Genetic modifications in microbes, while improving efficiency, also raise concerns about long-term environmental impacts. Furthermore, equitable access to microbial technologies must be ensured, preventing monopolisation by large corporations that could restrict access to small-scale farmers and developing nations.
Ultimately, while microbes hold immense potential for sustainable food production, the responsible development and deployment of these technologies will be crucial in addressing both ethical concerns and practical challenges.
